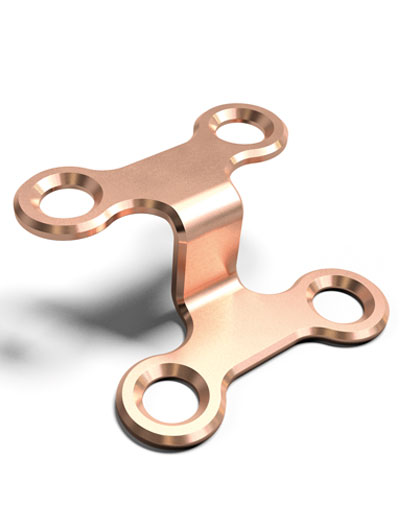
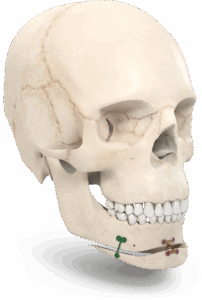
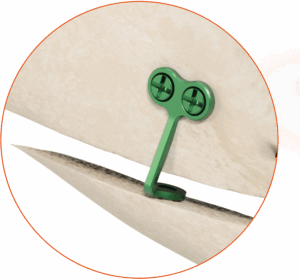
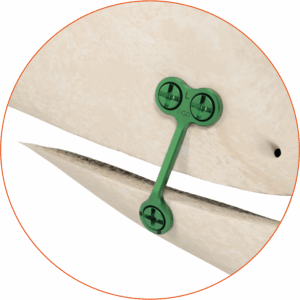
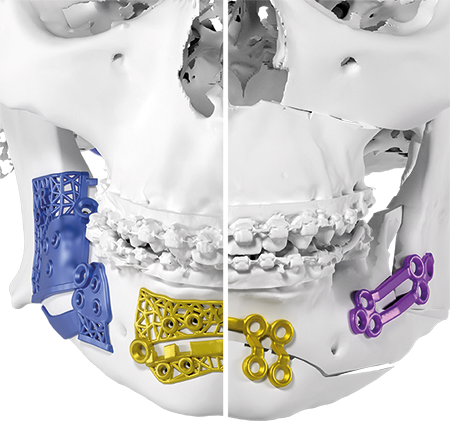
The Chin Wing genioplasty is a continuous basilar osteotomy that allows repositioning of the mandibular line from the right to the left angle, with three-dimensional correction of projection, height, and mandibular inclination.
This technique ensures harmonious and stable reshaping of the lower third of the face while preserving bone continuity.